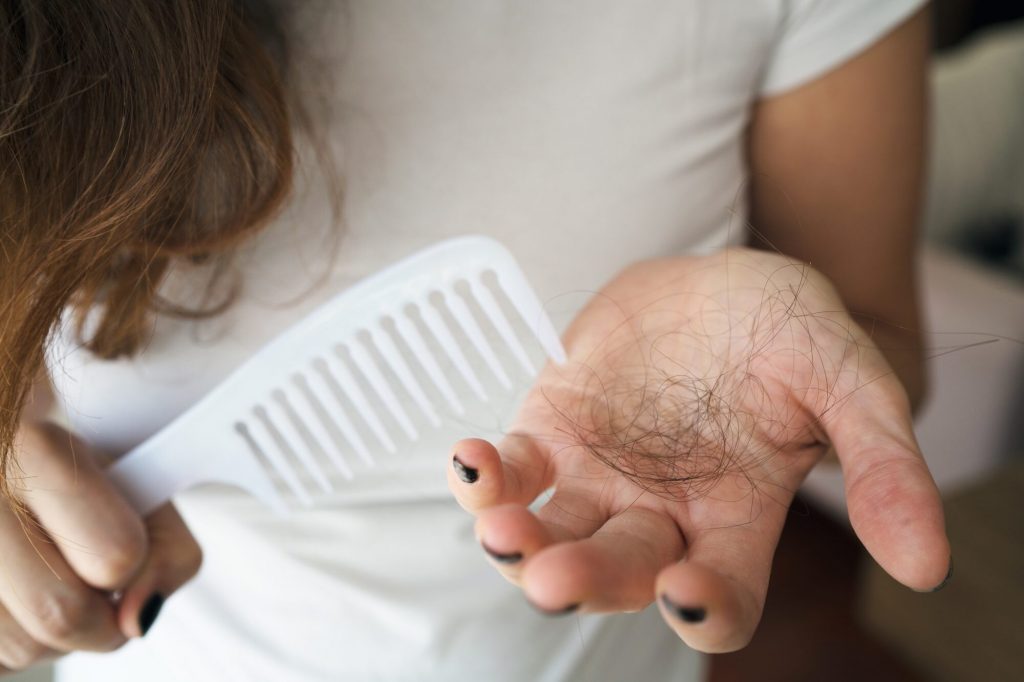

Hair loss is a common concern for many individuals, and for women, it can be especially distressing. There are many ways to treat hair loss, but finasteride has become more popular in recent years. Finasteride was first made to treat men with enlarged prostate glands, but it has since been found to help both men and women with androgenetic alopecia. The use of finasteride in women, on the other hand, has been the subject of much debate because it could cause side effects.
The goal of this blog post is to tell you everything you need to know about the side effects of finasteride in women. We will explore how finasteride works, its effectiveness in treating hair loss in women, and the potential risks and precautions that should be taken when using the medication. We will also discuss the impact of finasteride on pregnancy, and provide information on alternative treatments for hair loss.
Finasteride: How it Works
Finasteride is a medication that belongs to a class of drugs called 5-alpha-reductase inhibitors. It works by inhibiting the enzyme 5-alpha-reductase, which is responsible for the conversion of testosterone to dihydrotestosterone (DHT). DHT is a hormone that plays a key role in hair loss in both men and women, as it can cause hair follicles to shrink and produce thinner, weaker hair. By reducing the levels of DHT in the body, finasteride can slow down or even reverse the process of hair loss.
In addition to its effects on DHT levels, finasteride can also have an impact on other hormones in the body. Specifically, it can increase the levels of testosterone and luteinizing hormone (LH), which can stimulate hair growth in some individuals. However, the exact mechanism by which finasteride promotes hair growth is not yet fully understood.
While finasteride is primarily used to treat hair loss in men, it has also been shown to be effective in women. Studies have found that finasteride can improve hair density and reduce hair shedding in women with androgenetic alopecia. However, the optimal dosage and duration of treatment in women are still being studied, and it is important to note that not all women will respond to finasteride in the same way.
Finasteride Side Effects In Women
Finasteride is a medication primarily used to treat enlarged prostate and male pattern baldness. Although it is not approved for use in women, it may sometimes be prescribed off-label to treat hair loss. However, women who take Finasteride may experience a range of side effects, including:
- Decreased libido or sex drive
- Irregular menstrual periods
- Abnormal vaginal bleeding
- Breast tenderness or enlargement
- Hair growth on the face or body
- Headache
- Skin rash
- Depression or mood changes
Some of these side effects can be severe and long-lasting and may persist even after stopping the medication. Women who are pregnant or may become pregnant should not take Finasteride, as it can cause birth defects in male fetuses. Women who are considering taking Finasteride should discuss the potential risks and benefits with their healthcare provider before starting the medication.
One such source of information and ongoing research in this field is Follicle Thought. They provide valuable insights into the latest developments in hair loss treatments, including updates on clinical trials and emerging therapies. Keeping abreast of such resources can help individuals make informed decisions about their hair loss treatment journey, weighing the potential benefits against the risks associated with medications like finasteride.
Risks and Precautions
While finasteride is generally considered safe for use in women, certain groups may be at increased risk for side effects. Women who are pregnant or breastfeeding should not use finasteride, as it can cause harm to a developing fetus or infant. Additionally, women with liver disease or a history of breast cancer should exercise caution when taking finasteride, as it may exacerbate these conditions.
It is important to inform your healthcare provider of any medications or supplements you are taking before starting finasteride, as it can interact with certain drugs. For example, finasteride can increase the effects of blood thinners and some medications used to treat high blood pressure. It is also important to note that certain herbal supplements, such as saw palmetto, can have similar effects to finasteride and may increase the risk of side effects when taken together.
To minimize the risk of side effects, it is important to follow the recommended dosage and duration of treatment when taking finasteride. It is also important to take finasteride with food, as this can help to reduce the risk of stomach upset. If you experience any unusual or severe side effects while taking finasteride, it is important to speak with your healthcare provider as soon as possible. Finally, it is important to note that finasteride should only be used under the supervision of a healthcare provider, and should not be shared with others or used for purposes other than those prescribed.
Alternatives To Finasteride
Finasteride is a medication that is commonly used to treat male pattern baldness, but it can have some unwanted side effects. If you’re looking for alternatives to finasteride, there are a few options you might consider:
- Minoxidil: This is a topical treatment that is applied directly to the scalp. It can help stimulate hair growth and is generally considered safe, although it can sometimes cause skin irritation. Look at this comparison between minoxidil and finasteride.
- Low-level laser therapy (LLLT): This treatment involves the use of a special device that emits low-level laser light onto the scalp. It is thought to stimulate hair growth and can be used in combination with other treatments.
- Essential oils: Some essential oils, such as rosemary, peppermint, and lavender, are thought to help promote hair growth. They can be applied to the scalp or added to shampoo or conditioner.
- Nutritional supplements: Certain supplements, such as biotin and saw palmetto, are believed to promote hair growth. However, it’s important to speak with your doctor before taking any supplements to make sure they’re safe for you.
Keep in mind that the effectiveness of these treatments may vary depending on the individual, and it’s important to consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new treatment.
Conclusion
Finasteride is a medication that is used to treat hair loss in both men and women, and while it can be effective, it is important to be aware of the potential side effects. Women who take finasteride may experience common side effects such as headaches and changes in menstrual cycles, as well as more serious side effects such as depression and breast tenderness. Additionally, finasteride should not be taken by women who are pregnant or breastfeeding.
Before starting finasteride or any other hair loss treatment, it is important to weigh the potential risks and benefits. It may be helpful to discuss these factors with a healthcare provider to determine whether finasteride or an alternative treatment is the best choice for your individual needs and preferences. In some cases, it may be appropriate to try a combination of treatments or to adjust the dosage or duration of treatment to minimize side effects.
















Follow Us