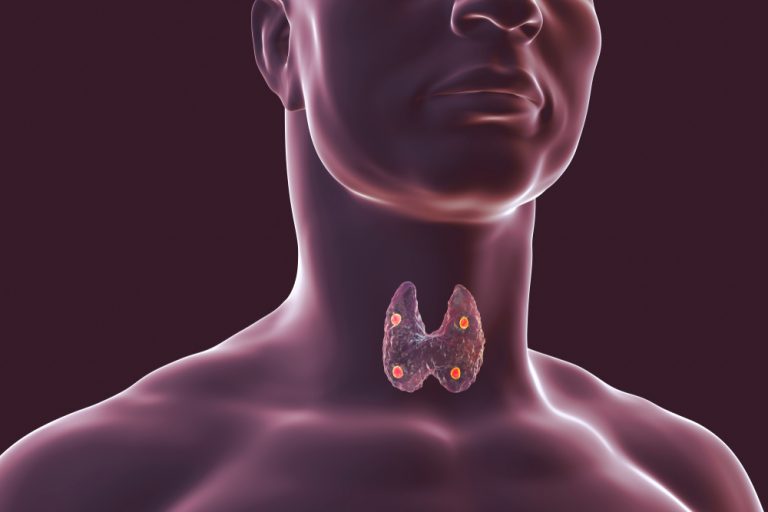
Hyperparathyroidism is a growth on the parathyroid glands resulting in an overproduction of calcium-regulating hormones called PTH.
There are four parathyroid glands, two on each side of the trachea or windpipe near where it splits into the left and right bronchi.
There is no known cause for this condition, although it is genetic. It can affect just one gland or all four glands. Hence, it is advisable to visit an expert surgeon to treat hyperparathyroidism to ensure you get the best treatment for this condition.
Symptoms typically include renal stones, kidney damage, decreased phosphate levels in the blood (hypophosphatemia), fatigue, muscle weakness, anxiety, and irritability.
As with any medical condition causing similar symptoms, hyperparathyroidism is diagnosed through a combination of medical history, physical examination, and laboratory tests.
Gland Assessment
The gland assessment is a procedure that can help diagnose hyperparathyroidism.
It involves the injection of a radioactive tracer into the bloodstream, which is then filtered by the kidneys and excreted in the urine.
It allows the doctor to see if there is an overproduction of PTH by looking for an increase in the activity of the parathyroid glands.
If you witness some, or all, of the symptoms of hyperparathyroidism, it is important to see your doctor for a diagnosis. It will help you take steps to resolve the problem at an early stage.
Your doctor will likely do a physical examination and order some laboratory tests to help make a diagnosis. If medication is not effective in controlling symptoms, surgery may be necessary.
Six Steps in Treatment of Hyperparathyroidism
According to a 2013 study reported by the National Library of Medicine, primary symptoms of hyperparathyroidism were seen in around 34-120 women per 1,00,000 in California.
Here are the five ways to treat this parathyroid gland disorder.
1. Diet and lifestyle changes
2. Medication
3. Parathyroidectomy surgery
4. Calcium and vitamin D supplements
5. Dialysis or renal transplant
6. Monitoring after treatment is completed
Diet and lifestyle changes: It is essential to eat a healthy diet that includes plenty of fruits, vegetables, legumes, and whole grains. Drinking plenty of water is also essential to prevent kidney stones from forming.
Medication: Medications are used to control the overproduction of PTH by interfering with hormone production or breakdown. It allows the calcium level in the blood to reach an acceptable range without causing adverse side effects on other organs.
Parathyroidectomy surgery: If medication fails to control symptoms, surgical options are available, with parathyroidectomy usually the best option.
Calcium and vitamin D supplements: Once treatment has begun, calcium is recommended for eight weeks post-surgery. Vitamin D helps absorb calcium, so it makes sense that they should be taken together.
Dialysis or renal transplant: If the kidneys can no longer filter the blood, dialysis or a renal transplant may be necessary.
Monitoring after treatment is completed: Once treatment is completed, it is essential to monitor calcium levels and PTH levels to ensure they remain within a healthy range.
If levels start to creep outside that range, steps may need to be taken to adjust the treatment plan.
When Do You Need to See a Doctor for a Minimally Invasive Parathyroidectomy?
If you are facing some, or all, of the symptoms of hyperparathyroidism, it is essential to see a doctor who specializes in treating hyperparathyroidism.
Early diagnosis and treatment are the keys to preventing more severe problems down the road. Your local doctor will do a physical examination and order some laboratory tests to help make a diagnosis. Depending on the results, they will then recommend the next steps.
The minimally invasive parathyroidectomy surgery is a safe and effective treatment for hyperparathyroidism. It involves the removal of the diseased gland(s) by entering through a small incision in the neck.
This procedure’s recovery period is shorter than an open parathyroidectomy.
Parathyroidectomy Surgical Steps
The minimally invasive parathyroidectomy surgery is a safe and effective treatment for hyperparathyroidism. It involves the removal of the diseased gland(s) by entering through a small incision in the neck. This procedure’s recovery period is shorter than an open parathyroidectomy.
Incision
The doctor will make a minor incision in the neck to enter the surgical area. The incision will be about 1-2 inches long.
Camera
A camera will be inserted through the incision to help the surgeon see the surgical area.
Laser
A laser will help remove the diseased gland(s).
Clamps
Tweezer-like clamps will be used to hold the gland(s) in place while they are being removed.
Sutures
The doctor will close the wound with sutures and wrap it up with a bandage.
If you are experiencing some, or all, of the symptoms of hyperparathyroidism, it is important to see your doctor for a diagnosis. After an early assessment and lab test, your doctor will start primary treatment. If medication is not effective in controlling symptoms, surgery may be necessary.
















Follow Us