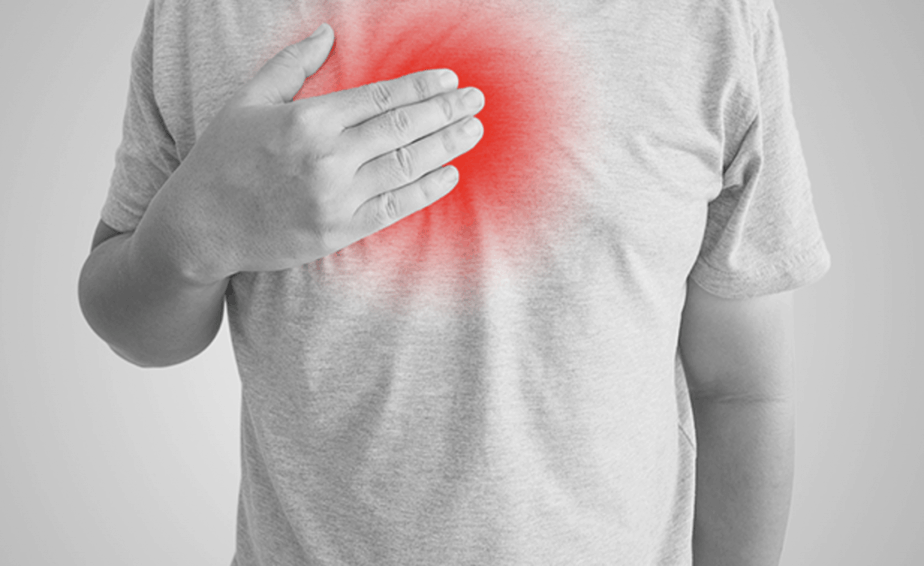
Coronary artery disease is a condition affecting the arteries that supply blood to your heart, known as your coronary arteries. When you have coronary artery disease or CAD, there’s a buildup of plaque that can narrow or block one or more of your arteries. The most common symptom of CAD is chest pain, known as angina.
Coronary artery disease is the most frequently seen cause of congestive heart failure. Below we’ll talk more about risk factors for coronary artery disease and what you should know broadly about this condition.
An Overview
Coronary artery disease is the most common heart disease in the U.S. It’s also sometimes referred to as ischemic heart disease.
The plaque that builds up in the walls of the coronary arteries is made up of cholesterol and other substances. Plaque buildup can cause your arteries to get narrower over time, which is known as atherosclerosis. Eventually, the blood flow may be partially or completely blocked.
When someone has coronary heart disease, their arteries aren’t able to deliver enough oxygen-rich blood to the heart. Around 18.2 million adults in America have coronary heart disease.
Risk Factors
There are certain lifestyle factors playing a role in developing coronary artery disease, including eating an unhealthy diet, being overweight, or being physically inactive. Smoking is also a risk factor.
If there’s a family history of heart disease, it can increase your risk, particularly if you have a family history of someone with heart disease developing at age 50 or younger.
High blood pressure, high cholesterol, as well as diabetes, are other risk factors.
You can reduce your risk of coronary artery disease by eating a healthy diet, regularly exercising, and reducing the amount of sugar you eat. You should also stop smoking.
Symptoms
As mentioned, angina, which is chest discomfort, is the most frequently seen symptom of coronary artery disease. People describe angina in different ways. Some people say it’s painful, and others experience heaviness or tightness. You might also experience burning or squeezing, and the symptoms can be mistaken for indigestion or heartburn.
Other possible symptoms can include shoulder or arm pain, shortness of breath, sweating, and dizziness.
If someone has coronary artery disease and a blockage almost entirely or completely cuts off their blood flow, the heart muscle starts to die, which is a heart attack.
Women can experience the symptoms named above but are also more likely to have back pain, jaw pain, nausea, and vomiting. They may also experience shortness of breath without chest pain.
Diagnosis
A healthcare provider will go over someone’s medical history, do a physical exam, and will likely conduct a variety of other tests to make a diagnosis.
Tests used to diagnose CAD include:
- Electrocardiogram, which monitors electrical signals traveling through the heart.
- Echocardiogram, using ultrasound waves to create an image of the heart.
- A stress test measures the stress on the heart while doing physical activity and while at rest.
- Cardiac catheterization, where a doctor injects dye into the coronary arteries through a catheter that helps identify blockages.
- A heart CT scan is where a doctor can check for deposits of calcium in the arteries.
Treatment
If you’re diagnosed with coronary artery disease, it’s important that you work on reducing or controlling risk factors. You also need treatment because getting it promptly can lower the risk of stroke or heart attack.
Treatment will depend on your overall health, as well as other conditions you might have.
Medications are the most frequently used treatments for CAD. Your healthcare team will also likely recommend that you make lifestyle changes.
If medication and lifestyle changes don’t improve your condition, your doctor might recommend procedures that will increase blood flow to the heart.
These procedures can include a balloon angioplasty used to widen blocked arteries. A coronary artery bypass graft surgery requires open chest surgery, and there’s something called an enhanced external counterpulsation. With this procedure, there’s the stimulation of new blood vessels to bypass a clogged artery. This isn’t an invasive procedure.
The outlook for coronary artery disease depends on the person. Your best chances of preventing severe heart damage require that you take action early on and implement lifestyle changes along with following your doctor’s treatment plan.
You’ll need to keep up with any medicines that are used to treat risk factors for CAD, like blood pressure medicines. Your healthcare team might also provide you with specific lifestyle changes to make that are relevant to you, your situation, and your health.
















Follow Us